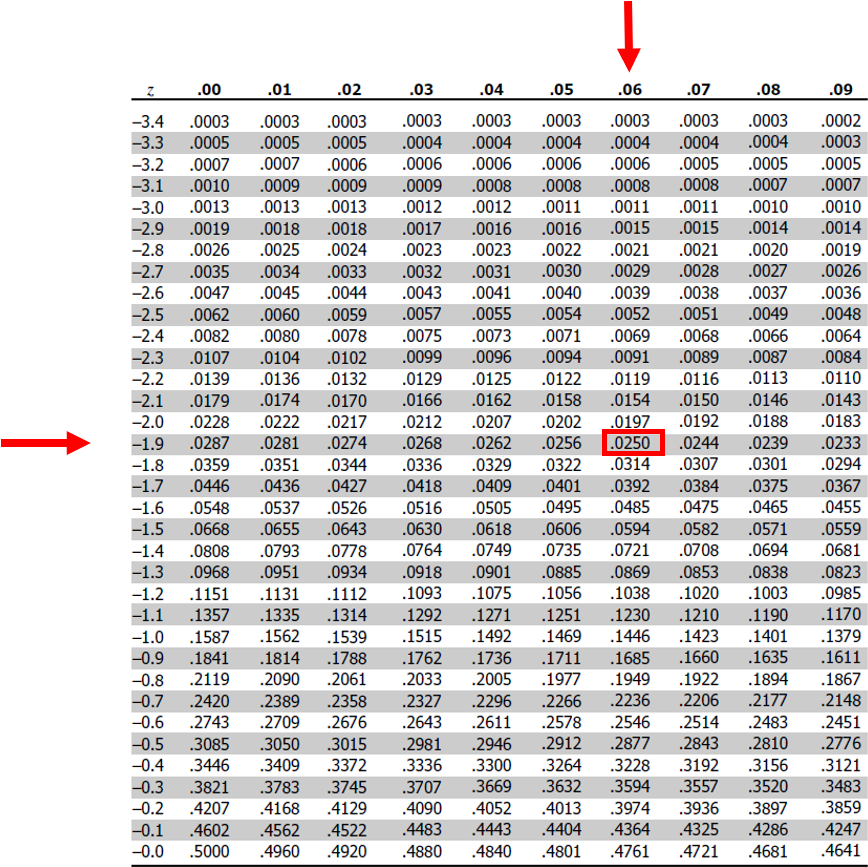
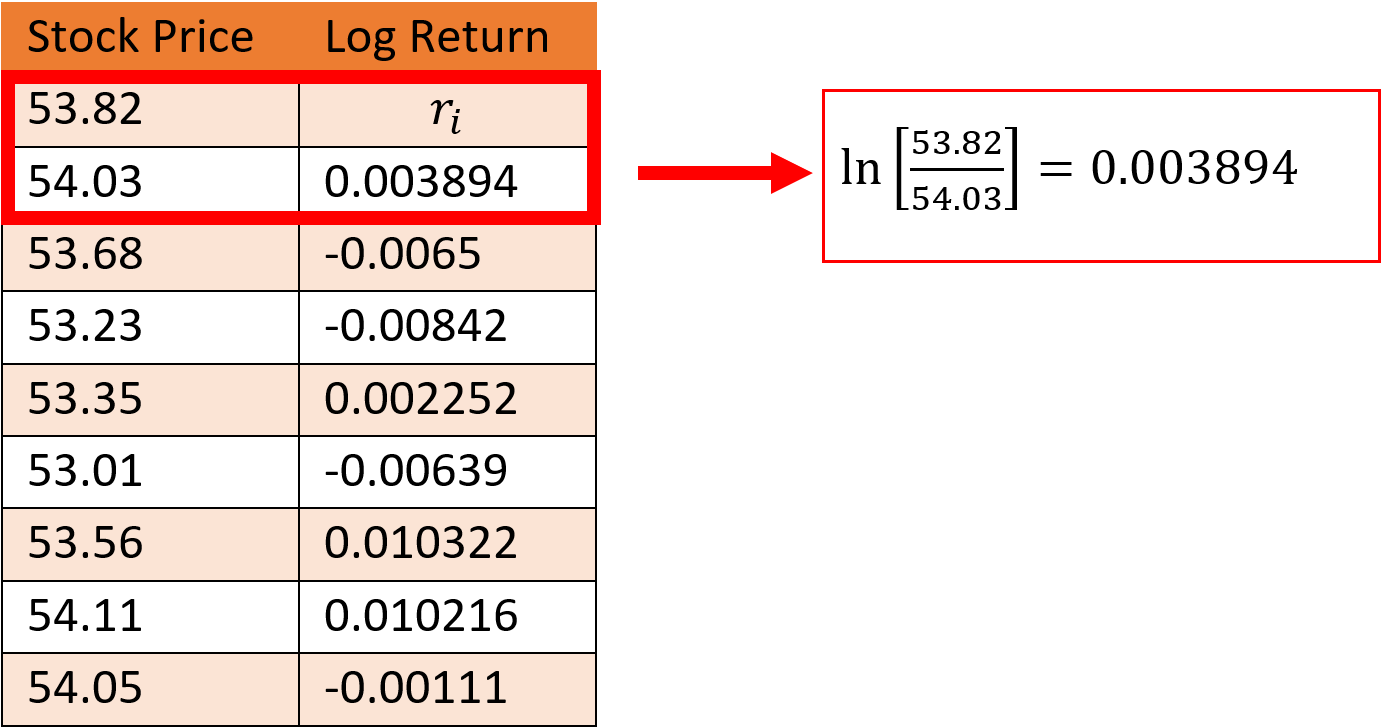
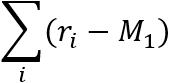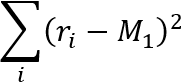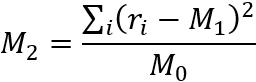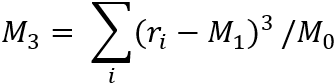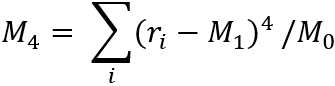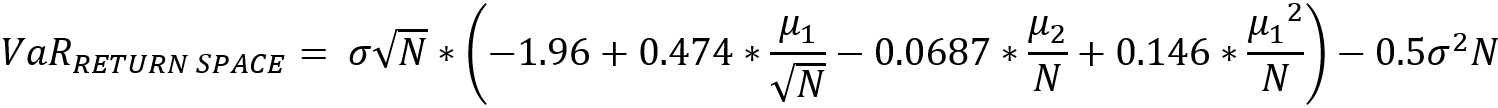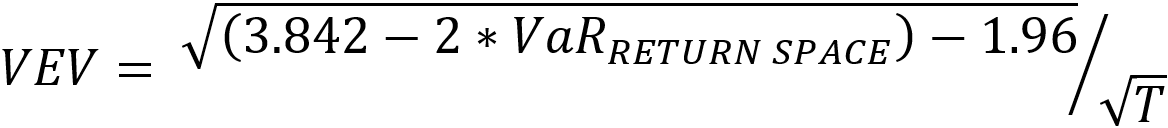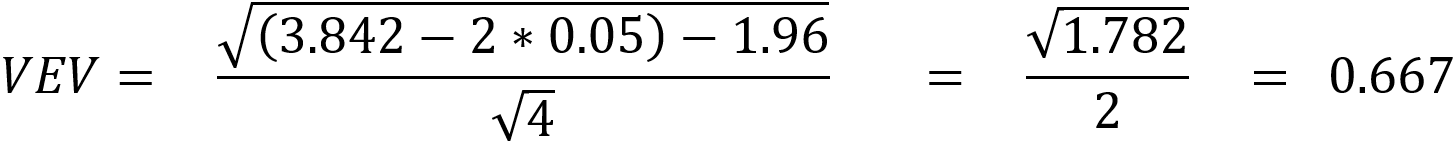This section outlines the process of calculation of the VaR Equivalent Volatility (VEV) which is used in the calculation of MRM for Category 2 PRIIPs.
This calculation embraces the concept of the Cornish-Fisher Expansion method which transforms the Value at Risk (VaR) calculation into a volatility risk measure.
Once calculated, this VaR Equivalent Volatility (VEV) number is then assigned to a market risk measure (MRM) category ranging from a scale of 1 to 7. For example, a VEV of 10% would place the security into an MRM Class of 3.
An MRM Class of 1 contains those securities with the lowest risk, while a class of 7 would indicate the highest risk category.